In recent years, the 3D anatomy model has emerged as a groundbreaking tool in the fields of medicine, education, and research. Unlike traditional two-dimensional textbooks and static anatomical diagrams, these models offer a dynamic and interactive experience that enhances the learning and teaching process. As technology continues to advance, students and professionals alike are turning to this innovative method to deepen their understanding of the human body.
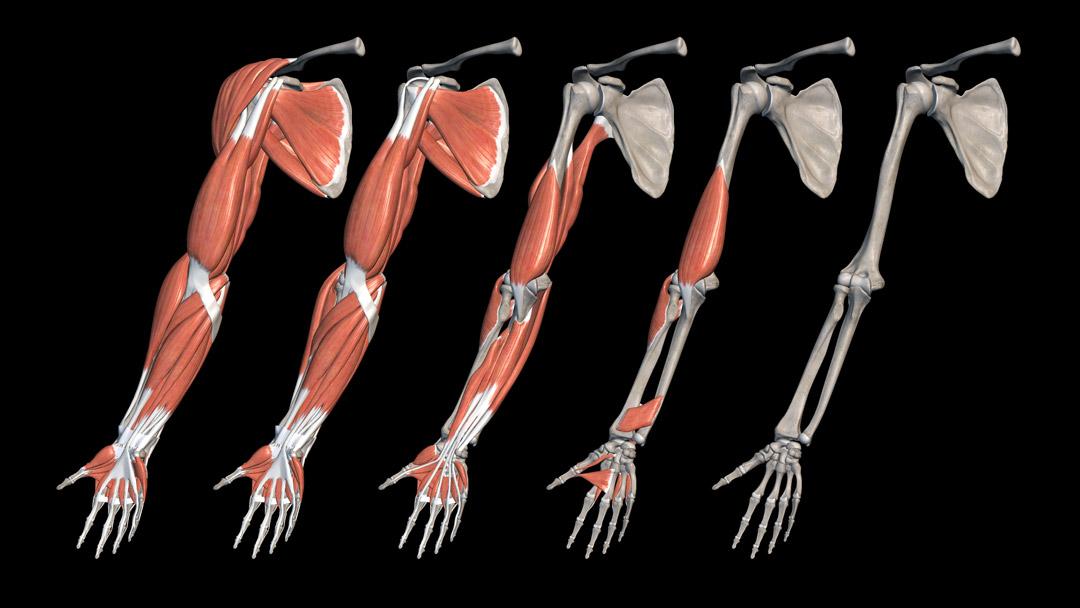
The use of a 3D anatomy model allows for a detailed exploration of human structures that were once difficult to visualize in full. From muscles and bones to organs and vascular systems, these models provide accurate representations that can be viewed from any angle. This capability enables learners to grasp spatial relationships within the body, which is a crucial aspect of anatomy that flat images often fail to convey.
Medical schools and universities have been early adopters of the 3D anatomy model, recognizing its potential to improve student engagement and comprehension. By incorporating interactive software and virtual reality platforms, these institutions provide students with immersive experiences that simulate real-life dissections. Such simulations allow for repeated practice without the limitations of cadaver availability, making the 3D anatomy model a practical and ethical teaching solution.
One of the key advantages of the 3D anatomy model is its adaptability across various learning styles. Visual learners benefit from color-coded structures and 360-degree views, while kinesthetic learners can manipulate the model to explore different anatomical layers. Auditory learners can supplement their exploration with guided narration or integrated video explanations, making the model a truly inclusive educational tool.
In addition to academic settings, healthcare professionals use the 3D anatomy model as a reference in clinical environments. Surgeons, for instance, can use it to plan complex procedures by studying anatomical variations and potential complications. Patient communication also improves when practitioners use the 3D anatomy model to explain diagnoses or treatment plans in a visual and accessible manner.
The development of mobile apps and online platforms has made the 3D anatomy model more accessible than ever before. Students no longer need to rely solely on lab time or physical models; they can now explore human anatomy from their tablets, laptops, or even smartphones. This level of accessibility supports remote learning and self-study, ensuring that learners can engage with anatomical content anytime and anywhere.
Beyond its educational and clinical applications, the 3D anatomy model is also being utilized in scientific research. Researchers can analyze detailed representations of anatomical structures, study abnormalities, and simulate physiological processes. The ability to model rare conditions or variations in anatomy makes the 3D anatomy model a powerful tool for advancing medical knowledge and innovation.
Technological advancements in artificial intelligence and augmented reality have further enhanced the capabilities of the 3D anatomy model. AI algorithms can now personalize learning paths based on a user’s progress, while AR features enable users to project life-sized anatomical models into their environment. These innovations are pushing the boundaries of what is possible in anatomy education and training.
Educational publishers and developers continue to invest in refining the 3D anatomy model, ensuring its accuracy and ease of use. High-resolution graphics, realistic textures, and real-time interaction contribute to a more authentic experience. As these models become increasingly sophisticated, they are expected to play a central role in shaping the future of medical education and healthcare delivery.
The global adoption of the 3D anatomy model is a testament to its effectiveness and versatility. Institutions across the world are incorporating this tool into their curricula, bridging the gap between theory and practice. Whether used in a classroom, operating room, or research lab, the 3D anatomy model is transforming how we understand and engage with the human body.
While the 3D anatomy model offers numerous benefits, challenges such as cost, technical requirements, and the need for training still exist. However, as demand grows and technology becomes more affordable, these barriers are likely to diminish. The ongoing collaboration between educators, software developers, and medical professionals will be key to overcoming these obstacles and maximizing the model’s potential.
In summary, the 3D anatomy model represents a significant leap forward in medical education and practice. Its ability to present the human body in a detailed, interactive, and accessible manner is revolutionizing how anatomy is taught and understood. As this technology continues to evolve, its impact will only grow, making the 3D anatomy model an indispensable resource in modern healthcare and education.
